Mohamad-Ali Salloum is a Pharmacist and science writer. He loves simplifying science to the general public and healthcare students through words and illustrations. When he's not working, you can usually find him in the gym, reading a book, or learning a new skill.
Ultrasound imaging: Beyond the Surface: A Deep Dive into the Inner Workings of Ultrasound Imaging
Share
The story of ultrasound exploration is one of invention and perseverance, driven by an attempt to discover the secrets of the human body. Researchers have pushed the boundaries of science to explore the potential of sound waves for medical imaging, from the creation of sonar technology during World War I and II through the pioneering work of Karl Dussik in Austria. This road of discovery has resulted in a revolution in medical practice, with ultrasound now being used to diagnose and treat a wide range of diseases. Join us on a fascinating tour through the history of ultrasound to see how this extraordinary technology has changed the appearance of modern medicine.
To begin, understanding how ultrasound works will help us appreciate the incredible power and promise of this remarkable technology. So, to begin, consider the following question:
What is the procedure of an ultrasound?
"Ultrasound imaging is based on the same principles involved in the sonar used by bats, ships, and fishermen," according to the Radiological Society of North America. When a sound wave meets an item, it bounces back, which is known as echoing. By detecting these echo waves, it is possible to calculate the object's distance as well as its size, form, and consistency (whether the thing is solid or fluid).
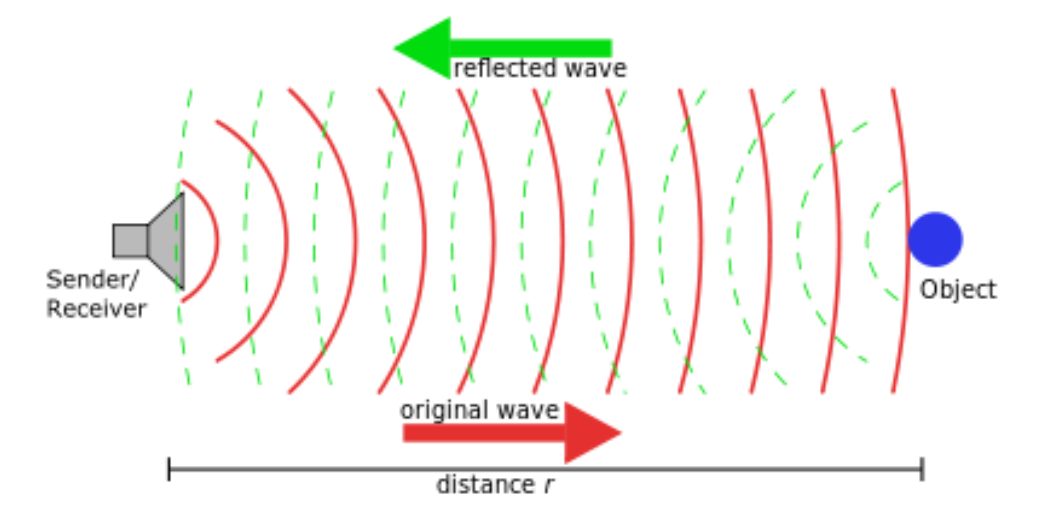
What are the other elements of this procedure, from bat technic to medicine?
Ultrasound can detect changes in the appearance, size, or form of organs, tissues, and arteries, as well as abnormal masses like tumors. Ultrasound imaging sends high-frequency sound waves into the body via a tiny transducer (probe). The probe records the noises that bounce back, and a computer uses the sound waves to generate an image. Because ultrasound tests do not employ radiation (like X-rays do), the patient is not exposed to radiation. Because ultrasound images are collected in real-time, they can show the structure and movement of the body's internal organs, blood moving through blood vessels, or an unborn baby's movement and heartbeat.
Now, let's investigate the technique's applications after we've learned about it.
Ultrasound is used for a variety of diagnostic and therapeutic purposes in medicine. Some of the most common reasons why ultrasound is used include:
- Medical condition diagnosis: pregnancy, heart illness, and cancer. Ultrasound imaging can offer clinicians detailed views of interior organs and structures, allowing them to detect any anomalies or disorders.
- Medical procedure guidance: biopsies and needle aspirations. Doctors can use ultrasound imaging to visualize the location of tissues and structures, allowing for more accurate and precise operations.
- Ultrasound can be used to track the advancement of medical disorders, such as the growth and development of a fetus during pregnancy or the progression of a disease.
- Therapy: Ultrasound can be used therapeutically to reduce inflammation and improve healing, such as in physiotherapy or sports medicine.
From the purpose to the safety, did you know that getting an ultrasound scan is one of the risk-free medical procedures? That's correct, it's safer than petting a grizzly bear or riding a unicycle blindfolded. So, if you want to keep out of trouble, just lie back, relax, and let the ultrasound do its thing!
However, we will state some of the potential side effects or complications of ultrasound scans:
- Patients may suffer discomfort or agony during the ultrasound scan in some situations, especially if the transducer is pushed against a sensitive portion of the body.
- Skin irritation: The ultrasonic gel used during the scan may cause skin irritation or allergic responses.
- Although there is no evidence that ultrasound scans are detrimental to babies, some research has suggested that repeated or prolonged exposure to ultrasound waves may have a deleterious effect on fetal development. As a result, ultrasound scans are often conducted only when medically essential during pregnancy.
- False positives or false negatives: As with any diagnostic test, there is always the potential for false positives or false negatives, which can lead to unnecessary follow-up treatments or missed diagnoses.
The discussion of false positive and false negative diagnoses may raise the issue of how accurate ultrasound scans are.
Ultrasound scans are often regarded as a very accurate imaging modality with high sensitivity and specificity for a wide range of medical disorders. The accuracy of an ultrasound scan can be affected by several factors, including the technician's competence and expertise, the quality of the equipment used, and the specific ailment being checked.
Ultrasound scans, in general, have been demonstrated to be highly accurate for diagnosing illnesses such as pregnancy, gallstones, and thyroid nodules, among others. As with any medical test, there is always the possibility of false positives or false negatives, which may necessitate additional testing or review.
In the ever-evolving landscape of modern medicine, ultrasound scans stand out as a shining example of the power of human innovation. From their humble beginnings in the early 20th century to their current status as a cutting-edge imaging modality, ultrasound scans have revolutionized the way we approach healthcare, providing a safe, non-invasive, and highly accurate means of visualizing internal structures and diagnosing medical conditions. As we continue to push the boundaries of what's possible in medical imaging and beyond, it's clear that ultrasound scans will remain a vital tool in the arsenal of healthcare providers around the world, offering a glimpse into the incredible complexity and beauty of the human body.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.elsevier.com/books/diagnostic-ultrasound-2-volume-set/rumack/978-0-323-40171-5
- https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/edit/10.1201/9780429195358/diagnostic-ultrasound-second-edition-john-mcgahan-barry-goldberg
- https://mifimaging.com/2018/04/05/how-does-an-ultrasound-work/#:~:text=Ultrasound%20imaging%20uses%20a%20small%20transducer%20%28probe%29%20to,there%20is%20no%20radiation%20exposure%20to%20the%20patient.
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/ultrasound-scan/#:~:text=An%20ultrasound%20scan%2C%20sometimes%20called,a%20surgeon%20during%20certain%20procedures
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24176149/
List of Services
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Mohamad-Ali Salloum, PharmD
Share
Recent articles: