Mohamad-Ali Salloum is a Pharmacist and science writer. He loves simplifying science to the general public and healthcare students through words and illustrations. When he's not working, you can usually find him in the gym, reading a book, or learning a new skill.
Seeing is Believing: The Incredible Impact of X-Ray Technology
Share
These strong rays have been used by doctors and scientists for almost a century to gaze into the mysteries of the human body and beyond. But did you know that X-rays were found entirely by chance?
In 1895, Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen, a German physicist, was experimenting with cathode rays (aka electric currents) when he noticed an unusual glow coming from a nearby screen. He had no idea that this unintentional discovery would forever revolutionize the world of medicine!
Radiation such as X-rays can travel through the body. They are invisible to the naked eye and cannot be felt.
The energy from X-rays is absorbed in varying rates by different regions of the body as they move through the body. After the X-rays have passed through, a detector on the other side of the body collects them and converts them into an image.
Dense portions of your body, such as bone, that X-rays find difficult to get through, appear as distinct white patches in the image. Softer tissues that X-rays can easily pass through, such as your heart and lungs, seem darker.
So, what’s the true purpose of X-rays?
They are commonly used for a variety of evaluations, of which we shall highlight a few:
- Dental X-rays are used in dentistry to obtain images of the teeth and surrounding tissues, which aid in the diagnosis of oral health concerns and treatment planning.
- Cancer Treatment: a type of radiation therapy that uses high doses of radiation to eliminate cancer cells in specific parts of the body.
- Veterinary Care: utilized in veterinary medicine to diagnose and treat animals, assisting veterinarians in the detection of fractures, cancers, and other health problems.
- Industrial inspection is used to inspect machinery and infrastructure in the industrial sector, assisting in the detection of flaws and the prevention of accidents.
- Forensic Science: a branch of forensic science that examines the evidence and reconstructs crime scenes to assist in identifying victims of crimes and accidents.
- Bone Density Testing: used to assess bone density and aid in the diagnosis of osteoporosis and other bone-related diseases.
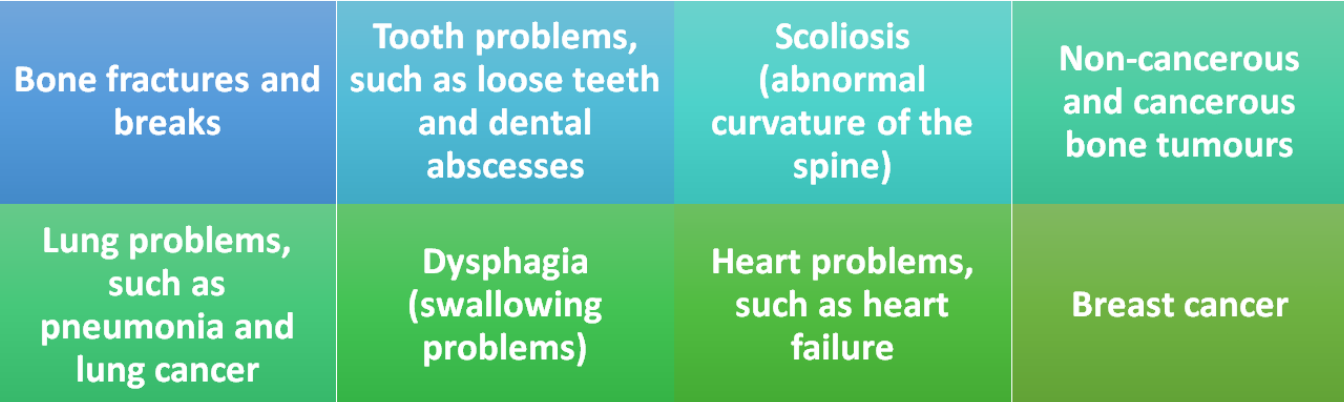
The chart below provides additional information about the medical applications of X-rays:
Finally, while X-rays are a useful tool for medical diagnostics, they can have negative side effects when used incorrectly or at high dosages. Patients should consider the risks and advantages of X-rays with their healthcare providers and only have imaging tests performed if they are medically necessary. Medical staff should also take precautions to limit their patients' exposure to radiation. X-rays, when used correctly and with safeguards, can provide vital diagnostic information without causing major harm.
Here are some of the side effects of X-rays that could be avoided:
- Skin Damage: Exposure to high doses of radiation can cause skin redness, itching, and even skin burns.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some patients may experience nausea and vomiting due to exposure to high doses of radiation.
- Cancer Risk: Long-term exposure to radiation can increase the risk of developing certain types of cancer, such as leukemia and thyroid cancer.
- Genetic Mutations: Radiation exposure can cause genetic mutations that may be passed down to future generations.
- Infertility: High doses of radiation can damage the reproductive organs, leading to infertility or other reproductive problems.
List of Services
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Mohamad-Ali Salloum, PharmD
Share
Recent articles: