Où la science rencontre l'art
Construire une communauté d'apprenants tout au long de la vie !
Bienvenue à Dopa Productions
Dopa Productions vous fournira des articles et des vidéos traitant de conseils de productivité et de connaissances médicales que tout le monde peut comprendre. En plus de cela, nos services incluent le tutorat en ligne, la création de contenu comme le montage vidéo et les modèles et animations 3D pour vos projets personnels, scolaires, universitaires ou professionnels. Nous pouvons également recevoir des demandes spéciales pour faire des services de production musicale.
Blog
À PROPOS
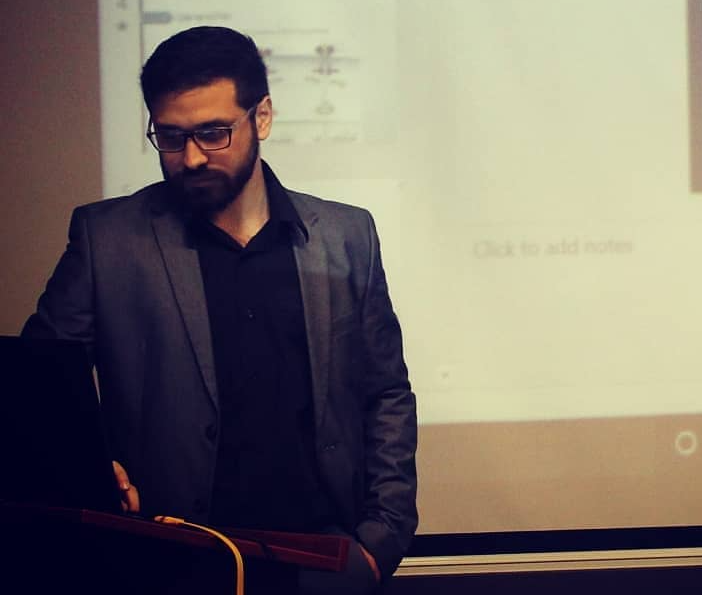
Fondateur
Salut. Je m'appelle Mohamad-Ali Salloum et je suis Pharmacien, YouTubeur et Créateur de Contenu avec un Diplôme de PharmD Clinique et un M2 en Recherche Clinique & Pharmaco-Epidémiologie.
Je me soucie beaucoup de la formation continue des personnes médicales et non médicales. Pour cela, j'ai commencé ce site Web pour partager mes connaissances sur les conseils de productivité qui m'ont permis de progresser dans ma vie et les informations médicales qui pourraient aider les étudiants à mieux comprendre les sujets et permettre aux non-médecins d'apprécier les sujets médicaux à travers un langage scientifique simple. Actuellement, je travaille dans le domaine de la recherche clinique.
Que pouvons-nous faire pour vous?
Modèles et animations 3D
- Explore and purchase 3D models for your work!
- You can also request a special model and animation for your personal or work use.
Musique
- Music has always been my mood stabilizer and especially the EDM. So I decided to learn how to make music!
Chaîne Youtube
- Dopa Productions started as a YouTube Channel where I do educational videos about health stuff.
- This channel will provide you with scientific information in the smoothest way possible.
Vous apprenez plus de l'échec que du succès.
Ne laissez pas cela vous arrêter. L'échec forge le caractère.
-Inconnue
Blog