Mohamad-Ali Salloum is a Pharmacist and science writer. He loves simplifying science to the general public and healthcare students through words and illustrations. When he's not working, you can usually find him in the gym, reading a book, or learning a new skill.
FDA pregnancy medication Labelling : Post 2015.
Share
Starting from 30 June 2015, the FDA implemented a new labelling rule for medications used during pregnancy and lactation.
As discussed in the previous article, the Categories published in 1979 (A, B, C, D, and X) were causing confusion for the patients and are increasing the risk to be misinterpreted by the health care professionals.
The new format is called the “Pregnancy and Lactation Labelling Rule” and is abbreviated as PLLR.
Using PLLR will remove some of the uncertainty that was caused by the previous five categories since it will contain a narrative information about the medication that will describe the potential risks of drug exposure based on available, evidence-based data. Ultimately, the new format will assist the health care professionals to assess the benefit versus risk when counseling pregnant women and nursing mothers who need the medication, and thus leading to enhanced protection of the mother and her baby.
After the PLLR was implemented, every pharmaceutical company that wants to register it’s new drug in the FDA, It should use the template provided by the FDA to include the required information in the leaflet.
Regarding the medications that were approved by FDA after 30 June 2001, The manufacturer was given from two to four years after 2015 to change the information on the leaflet as required.
Meanwhile, for the medications that were approved by the FDA before 30 June 2001, the format of the information was not required to be changed, however, It was mandated to remove the categorization that was assigned to this medication. The deadline for this action was 30 June 2018.
Concerning the OTC drugs, medications that can be given without a prescription, they were not affected by the new rule.
Not only the letter categorization was removed, the FDA also required the manufacturer to modify the sections in the leaflet.
The below picture will illustrate the modification on sections done between the 2 formats.
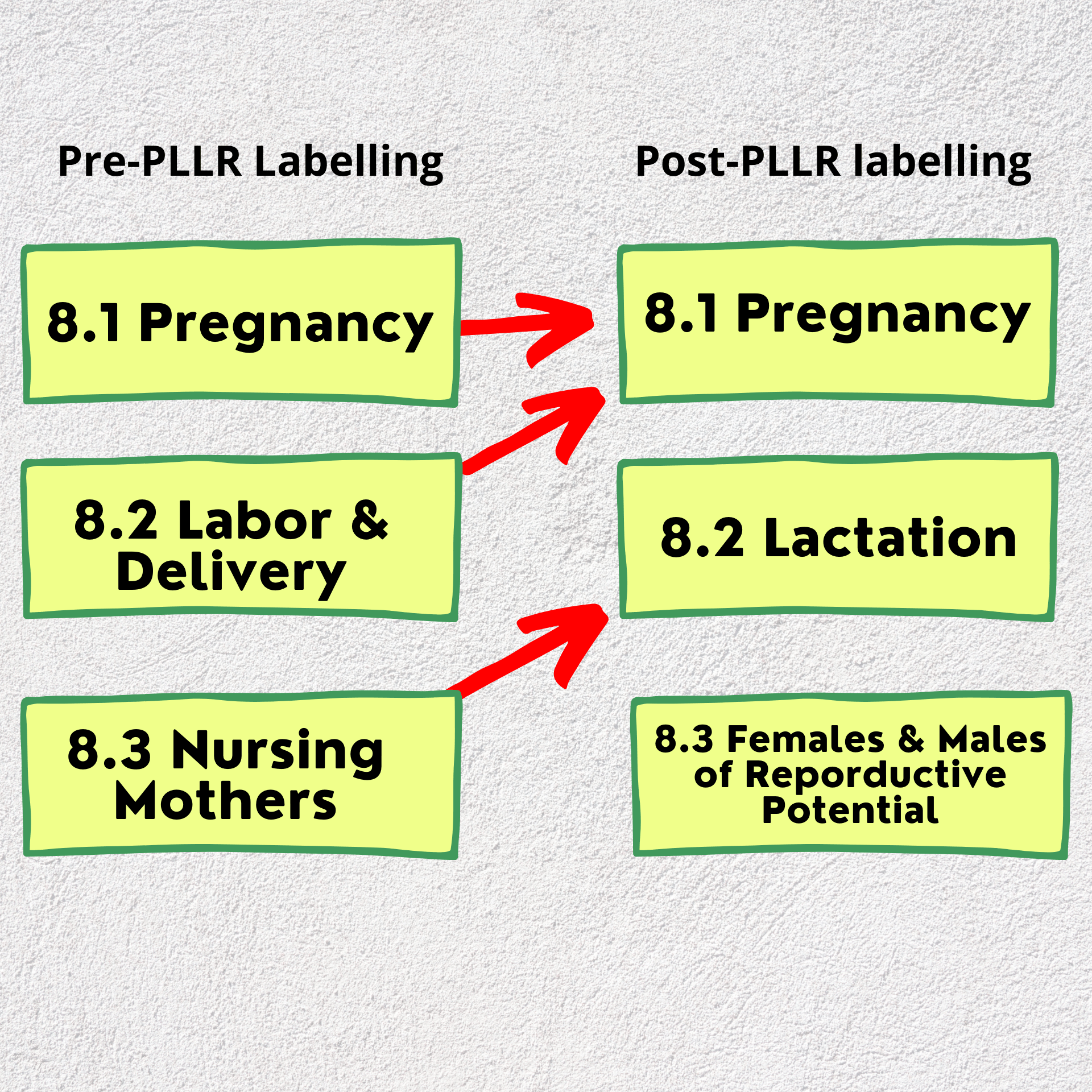
Briefly describing the change in the sections:
-The FDA decided to merge "Labor and Delivery" with the "Pregnancy" in section 8.1.
-Section 8.2 was named "Lactation".
-A new section was added, which is 8.3. and it described the information regarding the females and males of reproductive potential.
Speaking about this new section, it's very important to inform the physician about every drug that is being administered by the father or the mother of the baby. Also, if the couple were planning to have a baby, then they should discuss with the doctor about the drugs that being are being administered since a lot of drugs can remain in your body even after discontinuing it. (some medications can stay for weeks and even months in our bodies).
List of Services
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Mohamad-Ali Salloum, PharmD
Share
Recent articles: